Natural ventilation in an office building
 Project facts
Project facts
Type: Office, whole-building studies
Consultant: EQUA
Summary: Verification of a natural ventilation concept in a 60 000 m2 office building. Studies on air quality and a coupled comfort, energy and costs investigation was performed.
Challenge
In a 60 000 m2 office building, the peripheral offices are supplied with fresh outdoor air through openable flaps. Exhausted air is released through a central well. This exhausted air can optionally be driven naturally or mechanically. The function of this concept is verified by checking the air rates for all offices as well as the duration of natural and mechanical exhausted ventilation.
Solution
One ventilation sector of the building (app. 11 000 m2) was modelled with IDA ICE. The peripheral flaps as well as the central flap on the top of the well are modelled with controllable “large vertical opening” models. All other airflow resistances (office-corridor, corridor-well) are modelled with more simple “leak” models. The whole model contains 86 zones, 90 leaks and 105 large openings.Result
It was possible to show that the concept will work in principle, but needed some modification and calibration in the airflow path and its resistances as well as the control system. In addition to this, more detailed communication of expected air quality, as well as coupled comfort, energy and cost investigations was recommended.

Whole year duration diagram of CO2
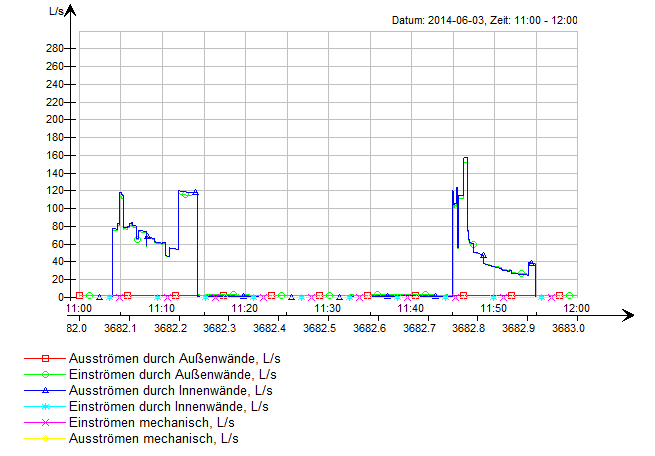
During an opening cycle of the peripheral flap: The air volume rate in the same zone varies due to the ventilation control of all other rooms of the same building sector.
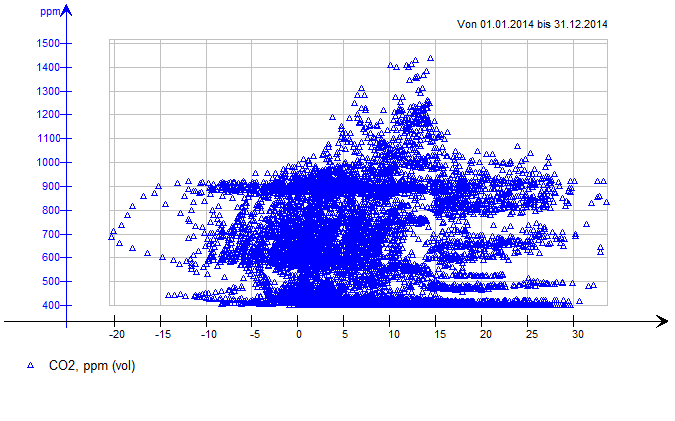
Hourly CO2 average depending on ambient air temperature. Natural ventilation rate decreases with increasing ambient air temperature. At 15°C, the central air exhausted is switched from natural to mechanical.

 English
English  Svenska
Svenska  Deutsch
Deutsch  Suomi
Suomi  中文(简体)
中文(简体) 
